Week by Week Pregnancy
İçindekiler
- 1 WEEKLY BABY DEVELOPMENT IN THE Womb
- 1.1 WEEK 1 and 2
- 1.2 THREE WEEKS
- 1.3 WEEK 4
- 1.4 WEEK 5
- 1.5 WEEK 6
- 1.6 WEEK 7
- 1.7 WEEK 8
- 1.8 WEEK 9
- 1.9 WEEK 10
- 1.10 11. WEEK
- 1.11 12. WEEK
- 1.12 WEEK 13
- 1.13 WEEK 14
- 1.14 WEEK 15
- 1.15 WEEK 16
- 1.16 WEEK 17
- 1.17 WEEK 18
- 1.18 WEEK 19
- 1.19 WEEK 20
- 1.20 WEEK 21
- 1.21 WEEK 22
- 1.22 WEEK 23
- 1.23 WEEK 24
- 1.24 WEEK 25
- 1.25 WEEK 26
- 1.26 WEEK 27
- 1.27 WEEK 28
- 1.28 WEEK 29
- 1.29 WEEK 30
- 1.30 WEEK 31
- 1.31 WEEK 32
- 1.32 WEEK 33
- 1.33 WEEK 34
- 1.34 WEEK 35
- 1.35 WEEK 36
- 1.36 WEEK 37
- 1.37 WEEK 38
- 1.38 WEEK 39
- 1.39 WEEK 40
WEEKLY BABY DEVELOPMENT IN THE Womb
While pregnancy is expressed in months among the public, doctors take the gestational week as a basis when evaluating the pregnancy process and watching the development of the baby in the mother’s womb. The day of the last menstrual period is considered the beginning of pregnancy and the total gestation period is calculated as approximately 280 days, that is, 40 weeks. In fact, fertilization, which is the beginning of pregnancy, occurs approximately 14 days after the first day of the last menstrual period. However, in practice, the date of the last menstrual period is accepted as the date of the start of pregnancy in order to make the timing correct.
WEEK 1 and 2
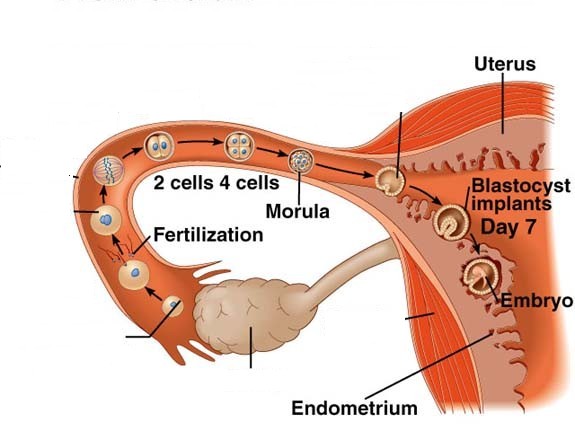
A group of egg cells that begin to develop in both ovaries in the first week try to become the largest egg with the highest chance of fertilization by entering a race among themselves. The egg that wins this race grows larger and larger than the other egg cells and becomes the “dominant follicle”. becomes. After a while, this dominant follicle cracks with the effect of some hormones and the egg inside is thrown into the abdominal cavity. After being thrown into the abdominal cavity, the egg caught by the tubes waits for fertilization for approximately 12-24 hours. If fertilization occurs (fertilization occurs with the union of egg and sperm cells), the first stage of pregnancy is passed. If fertilization does not occur, the egg dies, followed by menstrual bleeding approximately 14 days later. The days when the egg hatches, which coincides with the middle of the two menstrual periods, is the period when the woman’s chance of conception is highest. During this period, couples planning pregnancy should have sexual intercourse every other day or every other day. Since the chance of conceiving in one menstrual period is about 20%, couples who cannot get pregnant, Similarly, they should continue to have sexual intercourse in the next month, coinciding with their ovulation days, without disturbing their morale. In general, only 1 egg is produced and hatched in a woman during a menstrual period. Unlike fraternal twins and triplets, more than one egg develops and hatches, not a single egg. If all these eggs are fertilized, a multiple pregnancy occurs.
During all these events, the inside of the uterus, called the “endometrium” , began to thicken. The purpose of this thickening is to ensure that the fertilized egg (embrio) to be formed after fertilization occurs easily in the uterus. In other words, a bed is prepared in the womb for the tiny baby. Thus, blood supply increases in this part of the body in order to meet all the needs of the newly developing creature.
If fertilization occurs after the egg is cracked, the fertilized egg begins a long journey in the tubes that lasts for about a week. During the journey, the fertilized egg quickly changes shape and content. Chromosomes from both spouses combine in the egg cell, divide rapidly and multiply to form a cell cluster. After a while, this fertilized egg begins to divide. When the egg, which continues to divide in the form of 2,4,8 cells, reaches the uterus through the tubes, it has 32 cells and is called “morula”.
What your baby’s gender will be depends entirely on the X and Y chromosomes carried by your partner’s sperm cells. In other words, if your spouse’s sperm cell with the X chromosome fertilizes your egg cell, your child will be GIRL, and if the sperm cell with the Y chromosome fertilizes your egg, your baby will be a MALE. In other words, sex is determined during fertilization by the sperm carrying the X or Y chromosome.
THREE WEEKS
After the egg cell produced from the ovaries of the woman is fertilized with the sperm of the man, the embryo (baby) is formed. The embryo adheres to the thickened inner wall of the uterus approximately 7 days after fertilization (during this time, it has traveled through the tubes and reached the uterus).
WEEK 4
There hasn’t been any delays yet. Nowadays, the expectant mother can have a pregnancy test done in the blood or urine if she cannot menstruate.
The first sign of pregnancy is delayed menstruation. Nausea, morning sickness, and vomiting are other early symptoms. It is very effective to eat frequent and small meals and to have a light snack before getting up in the morning. Usually, these complaints disappear with the end of the first trimester (first 3 months). In addition, excessive cravings for certain foods and flavors, also called craving, can also be seen.
Although the expectant mother has not felt any change yet, the gestational sac (gestational sac) has begun to form and to carry oxygen and nutrients to the embryo thanks to the umbilical cord (passenger sac). The developing baby candidate now needs enough vitamins, folic acid, protein, calcium, iron, etc. from you. is waiting. You should start taking 400 micrograms of folic acid a day, especially a few months before conception.
WEEK 5
It is absolutely necessary to consult a doctor when vaginal bleeding or spotting is encountered. The bleeding seen may not be serious, but it should be evaluated for the possibility of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy. If you are complaining of cramping or abdominal pain, you should definitely consult a doctor. Gestational sac (gestational sac) should be seen in the uterus at the 5th week with transvaginal ultrasound. It reaches a size of approximately 1 cm. Meanwhile, the blood pregnancy test B-HCG is around 1500-2400. The gestational sac appears as a dark ring of about 8-10 mm in size within the thickened inner wall of the uterus and grows 1-2 mm per day. When the gestational sac reaches approximately 1 cm in size, the passenger sac begins to appear. Embryo and passenger sac are seen together in a gestational sac with an average diameter of 1.5 cm.
Meanwhile, the embryo is developing rapidly in the gestational sac. It is approximately 2-5 mm in size and is located close to the passenger’s pouch, which is observed in the form of a 3-4 mm round white ring.
WEEK 6
 Changes in the uterus and vagina can now be determined by gynecological examination. If there is no pregnancy nausea or vomiting, the expectant mother will gradually begin to gain weight. However, some weight loss due to nausea and vomiting does not usually have a negative effect on the baby. Generally, an average of 1 kg is gained in the first 3 months (12 weeks).
Changes in the uterus and vagina can now be determined by gynecological examination. If there is no pregnancy nausea or vomiting, the expectant mother will gradually begin to gain weight. However, some weight loss due to nausea and vomiting does not usually have a negative effect on the baby. Generally, an average of 1 kg is gained in the first 3 months (12 weeks).
WEEK 7
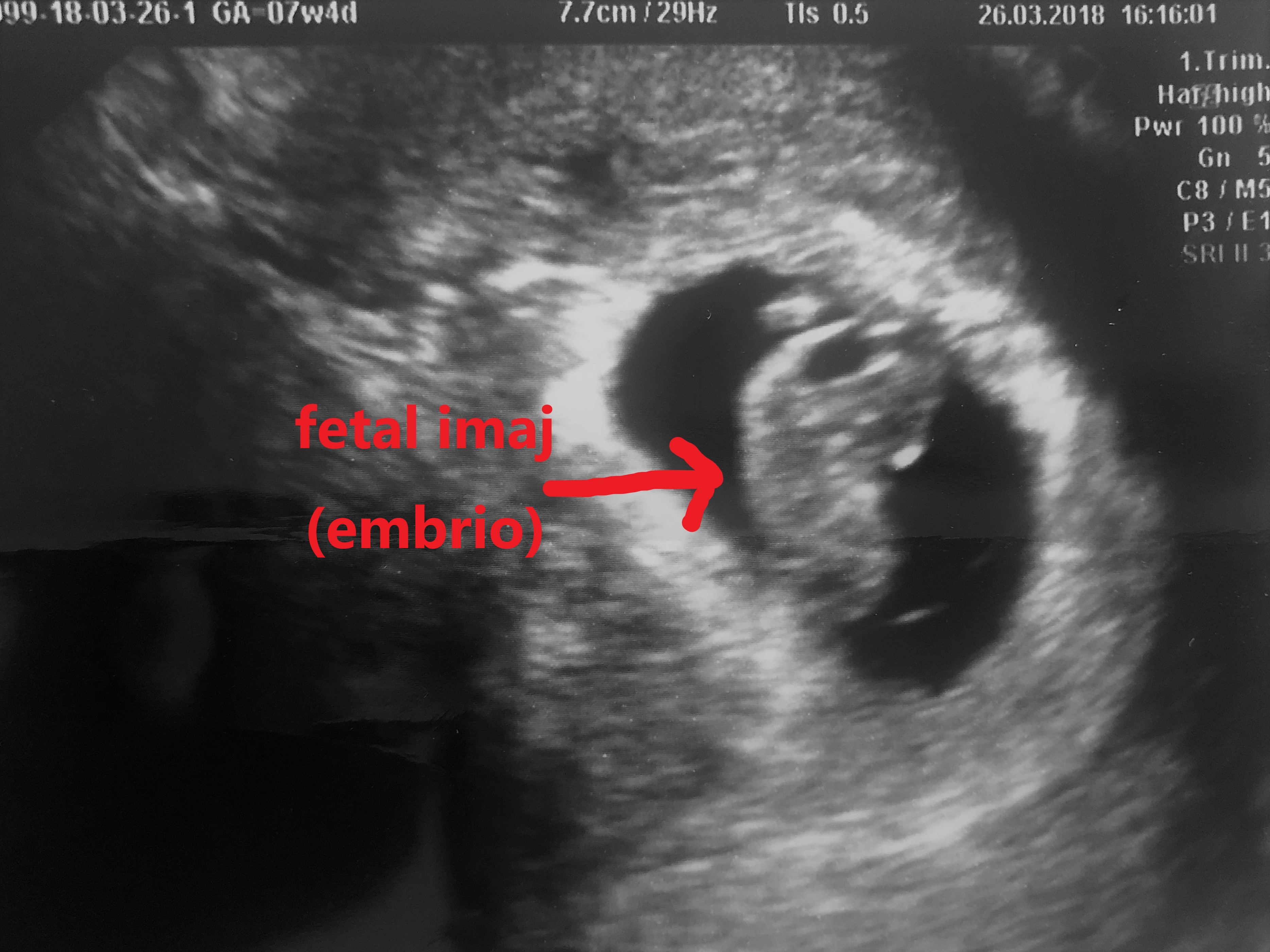 Now the expectant mother begins to feel changes in her body. Early pregnancy symptoms such as morning fatigue and craving became evident. There is fullness and tension in the breasts.
Now the expectant mother begins to feel changes in her body. Early pregnancy symptoms such as morning fatigue and craving became evident. There is fullness and tension in the breasts.WEEK 8
 While the uterus was the size of a fist before pregnancy, it has now reached the size of an orange. Depending on the growing uterus, there may be tension in the groin, lower parts of the abdomen and sometimes cramp-like pain. If the pain is very severe, you should definitely consult your doctor.
While the uterus was the size of a fist before pregnancy, it has now reached the size of an orange. Depending on the growing uterus, there may be tension in the groin, lower parts of the abdomen and sometimes cramp-like pain. If the pain is very severe, you should definitely consult your doctor.WEEK 9
The fetus can now be easily evaluated with both vaginal and abdominal (abdominal) ultrasonography. Head-butt length is about 2 to 3 cm. The embryo has acquired human form. Head, trunk, and extremities can be detected on ultrasound. The baby’s arm, leg and body movements can be seen on ultrasound. The fetus begins to move its extremities and trunk and can be seen somersaulting in the uterus. But the mother cannot feel it. It is not possible to see the gender.
WEEK 10
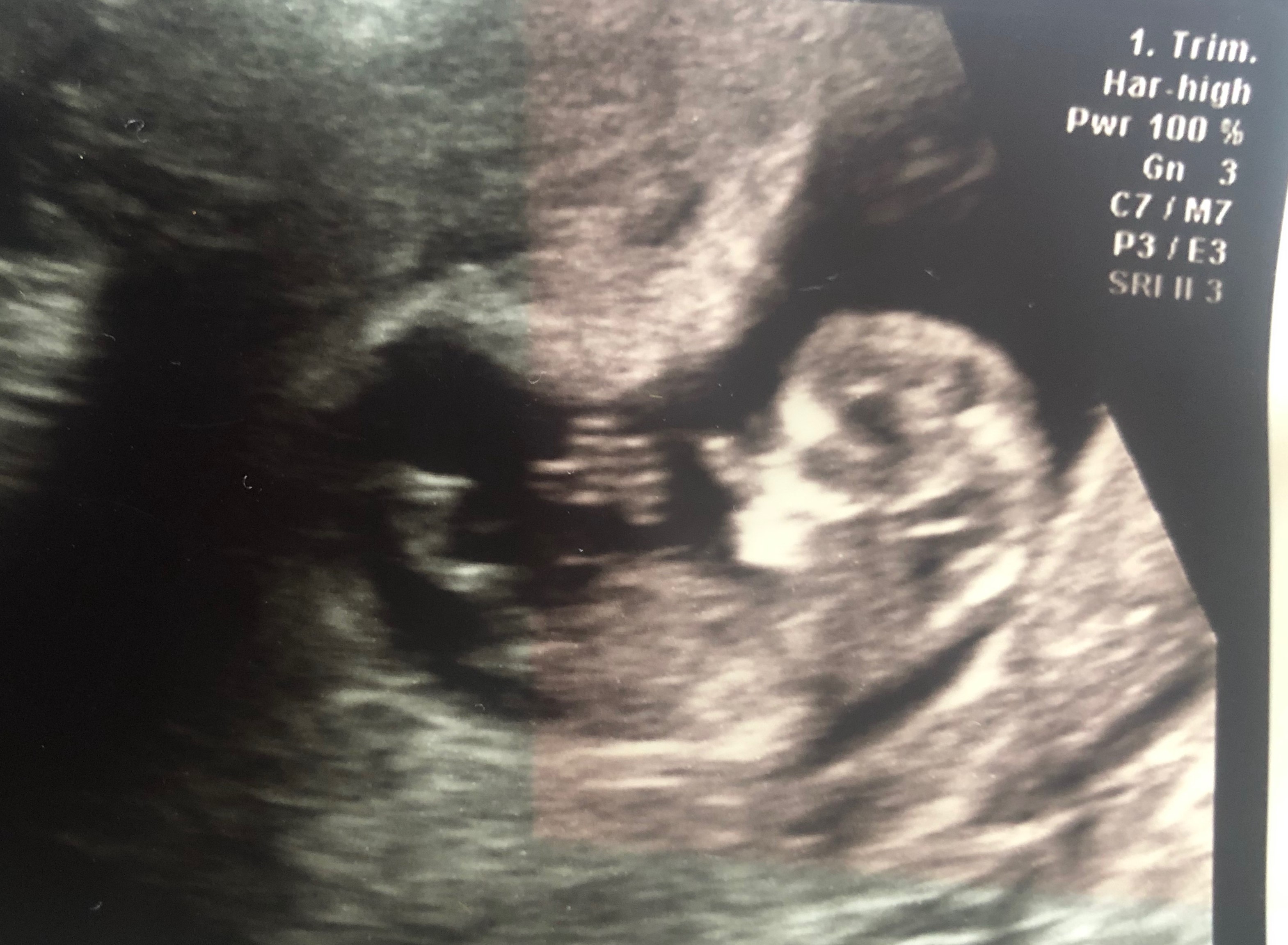 Pregnancy is still not obvious from the outside. However, the mother gradually begins to wear looser and looser clothes. Although the end is nearing now, emotional changes and craving continue.
Pregnancy is still not obvious from the outside. However, the mother gradually begins to wear looser and looser clothes. Although the end is nearing now, emotional changes and craving continue.The heart largely completes its development. Intestines developed outside the body move well into the abdominal cavity. Knees and feet become prominent. Toes and nails are visible. Muscles begin to gain strength. In girls, the clitoris develops, and in boys, the penis develops. His kidneys produce urine, arm and leg movements begin. Height: 5.5 cm. Weight: 6 gr. Since the formation of almost all joints and muscles is completed, the baby now moves in the water bladder, but it is not possible for you to feel these movements.
11. WEEK
In the mother, the uterus may be palpable in the lower abdomen. There may be changes in the mother’s gums, nails, and skin.
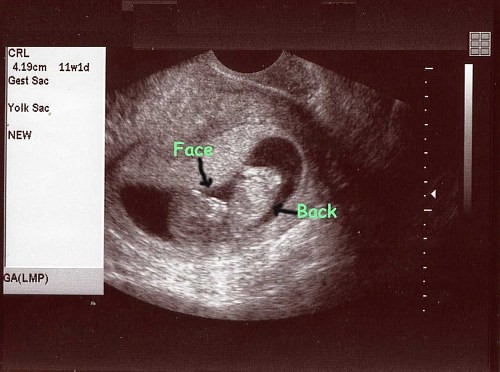
The most critical period of pregnancy is now over. In this week, the brain continues to grow rapidly and the head constitutes half of the fetus’s length. Its head and body are about the same size. Organ development is largely complete. The eyes of the fetus are closed and the iris layer continues to mature under these eyelids. As urine production begins in the kidneys, the amount of amniotic fluid in which it floats begins to increase, and this becomes approximately 50 ml per week. Although the baby kicks, the mother cannot yet feel it. Height: 7 cm. Weight 8 gr. 11-14 weeks dual screening test and nuchal thickness measurement, which is an early intelligence test, can be done from this week.
12. WEEK
Craving, nausea-vomiting and morning fatigue begin to decrease. You may have gained about 1-1.5 kg by this time.
The baby’s face has a human appearance, and the upper palate has begun to merge in the mouth. Hair follicles begin to appear in the facial skin. Fingernails begin to grow on hands and feet. In this week, all the internal organs of the baby are in working condition. She can pee. Nails develop. After this week, your baby is less likely to be harmed by drugs and harmful factors. The genitals are developed enough to reveal their gender. However, it may be possible to make this distinction in ultrasound, but the margin of error is high. Height: 8 cm, Weight: 18 gr.
11-14 weeks dual screening test and nuchal translucency measurement can be done.
WEEK 13
The early signs of pregnancy and the complaints it creates are almost absent. During this period, it is necessary not to get tired too much and rest as much as possible. As the uterus grows, it stretches and stretches the organs that surround it and the ligaments that hold it in place. This can be perceived as a mild groin pain. If you have not been able to gain weight due to nausea-vomiting, morning fatigue, etc., you will start to feel better and gain weight.
While the umbilical cord carries the necessary substances from the placenta to the fetus, it also transfers the waste materials from the fetus to the mother’s circulatory system.
Head-butt length is 6-8 cm. The head is larger than the body or as long as the body. The eyes are closer together, the appearance is more and more human-like. The intestines move to their normal places in the abdomen. Fingers and toes are fully formed, joints are working. The external genitalia are now visible.
WEEK 14
From the outside, you gradually begin to understand that you are now pregnant. You may experience mild pain in your lower back, constipation, and slight drops in your blood pressure. Nausea has passed, but with the relaxing effect of progesterone, stomach contents return to your esophagus (reflux) and burning may occur. Nutrition improves, your energy increases. Many women regain their lost sex drive during this period of pregnancy. If there are no complications, sexual intercourse is not prohibited during pregnancy.
Due to the rapid growth of the uterus, relaxation in the abdominal muscles, cracks in the skin (hip, abdomen, legs and breasts) (stria gravidarum) can be seen. Personal differences lie in the content of the connective tissue under the skin on the basis of skin cracks that occur during pregnancy. Because not every pregnant woman has stretch marks.
The baby’s head-butt length is 8-10 cm, and its weight is about 25 g. Ears come more forward and sideways from the back of the head. The chin becomes prominent. Your baby bends and straightens and shifts to external stimuli (when pressure is applied to the uterus with an ultrasound probe). Your baby is now swallowing and peeing.
WEEK 15
Your uterus can be felt 4-5 inches below your belly button. Amnios water increased and became 250 cc. It is understood from the outside that you are pregnant gradually. Due to your increased blood volume and ponding in the veins, nosebleeds may occur, varicose veins may occur in the legs.
When lying down, try to lie on your left side (if you are very uncomfortable, it can be on the right side). Because there may be a decrease in blood flow to the baby while lying on his back. If such a sleeping position makes you uncomfortable, you can put pillows between your back and legs. If varicose and hemorrhoids (hemorrhoids) etc. If you are having problems like this, raise your legs up to the level of your heart while resting (lying). If necessary, supportive compression stockings can be worn. A light colored liquid called clostrum may come from the breasts. This is a normal situation.
Your baby has started to drink amniotic fluid. Hiccups may be seen. Its height has increased to approximately 13 centimeters and its weight has increased to 75 grams. Fine, silky hairs called lanugo begin to appear on the developing baby’s head. These primitive hairs are lost at birth. During this period, the baby’s skin is quite thin and veins can be seen under the skin. Your baby has started to suck his thumb.
WEEK 16
 As your baby grows, it grows and expands in your womb. Your uterus weighs 250 grams and can be felt 4 fingers below the navel. Amniotic water is increasing and has been up to 250cc. After this week, if you have been pregnant before, you can feel the movements of the child, such as gas in the intestine or muscle twitching in the abdomen, which is called “revival” among the people. Experienced expectant mothers can feel the baby’s first movement this week. However, not feeling the movement does not mean that it is an abnormal situation. For those who have had their first pregnancy, this happens around the 20th week.
As your baby grows, it grows and expands in your womb. Your uterus weighs 250 grams and can be felt 4 fingers below the navel. Amniotic water is increasing and has been up to 250cc. After this week, if you have been pregnant before, you can feel the movements of the child, such as gas in the intestine or muscle twitching in the abdomen, which is called “revival” among the people. Experienced expectant mothers can feel the baby’s first movement this week. However, not feeling the movement does not mean that it is an abnormal situation. For those who have had their first pregnancy, this happens around the 20th week.
Gender is 12-14 in some cases. It can be seen in the last weeks of pregnancy, or not at all until the last stages of pregnancy, but this is a very rare situation. Determining the sex of the baby in these weeks mainly depends on the experience of the physician who performed the examination. Again this week, the triple screening test, which is extremely important in terms of down syndrome, can be performed. The ideal timeframe for this test is 16-18. for weeks.
The baby’s head – rump length is 10.75 – 11.5 cm. Its weight is about 140 grams. Nails are fully formed. On the head, fine hairs and feathers (lanugo) became more prominent. Nervous system development is largely complete. As a result of nerve impulses and the response of the muscles to them, thin hand, arm, leg and body movements are seen. Children’s heart sounds can be heard with a special stethoscope. Eyebrows and eyelashes are formed. Gender can be determined by ultrasound. Baby’s legs are now longer than their arms.
WEEK 17
Your appetite is getting better. The threat of miscarriage has decreased. Your load is not too heavy yet, your movements are not too restricted. You can communicate with your child by slowly listening to your baby’s movements. As the pregnancy grows, your partner can feel the child’s movements by placing his hand on your stomach.
Relaxation in the joints continues to increase. When getting out of bed, first sit down and then stand up with the help of your hands and arms. Do not carry unstable and heavy loads. When picking up something from the ground, take it by kneeling without bending from the waist. Do not try to reach (especially with one hand) items at heights from the shelves that you cannot reach with both hands.
The baby’s subcutaneous fat stores begin to increase rapidly from this gestational week. The baby’s sucking, swallowing and blink reflexes also appear during these weeks of pregnancy. The process of storing calcium in the baby’s bones is accelerated. He can suck his finger. This week, the baby’s heart is 30 liters a day. It pumps (about 1.5 buckets) of blood. At the end of this week, the height is 18 cm and the weight is 150 gr.
WEEK 18
 In parallel with the growth of the baby, the expectant mother begins to gain weight. It is quite normal to gain 2-4 kilos until these weeks. Your heart is working 30-50% more than before pregnancy.
In parallel with the growth of the baby, the expectant mother begins to gain weight. It is quite normal to gain 2-4 kilos until these weeks. Your heart is working 30-50% more than before pregnancy.
This week, the baby opens and closes his fingers and toes frequently. The first stool, called meconium, begins to form in the intestines from this gestational week. Prostate development in male infants begins and is completed this week. At the end of this week, the height is 20 cm and the weight is 210 g. With a detailed ultrasound examination (2nd level ultrasound) between this week and the 22nd week, very reliable information can be obtained about normal development, gestational age and the sex of the baby.
WEEK 19
 During this period, there may be mild pain due to the contraction of the growing uterus. Constipation, cramps in the legs, swelling in the joints, back pain may occur. With the effect of pregnancy hormones, redness can be seen on the face, shoulders and arms due to the enlargement of the small vessel ends.
During this period, there may be mild pain due to the contraction of the growing uterus. Constipation, cramps in the legs, swelling in the joints, back pain may occur. With the effect of pregnancy hormones, redness can be seen on the face, shoulders and arms due to the enlargement of the small vessel ends.
As of this week, a substance called vernix caseosa begins to be produced to protect the baby’s skin from the liquid environment to which it is constantly exposed. This substance is white in color, has a creamy consistency and protects the baby’s skin by covering it. Head – rump length is 13 – 15 cm, height is 22 cm, weight is 280 gr. The skin is transparent and the veins are visible underneath. Her hair is formed.
WEEK 20
 The uterus is at the level of your belly button. You may be sweating more than usual due to the overworking of the thyroid gland. Your waist gets thicker.
The uterus is at the level of your belly button. You may be sweating more than usual due to the overworking of the thyroid gland. Your waist gets thicker.
The baby’s nails, hair and eyelashes are formed, and organs can be easily selected in an ultrasonographic examination during this period. Most of its body is covered with a soft and hairy layer called lanuga.
In this week, rapid brain maturation begins after birth, which will continue until the age of 5 years. The baby’s senses of smell, taste, hearing, sight and touch begin to become more active.
The baby enters the periods of sleep and wakefulness in the mother’s womb. The mother begins to feel the baby movements. Height: 25 cm, Weight: 340 gr.
WEEK 21
If you haven’t started before, you should start iron support from this week. The iron you take with your diet will not be enough for you during pregnancy. For this reason, you should definitely get outside support.
In this period, waist and back pain can be seen due to the abdomen expanding forward in order to save space for the baby. Massage and hot application to the aching areas are recommended. The uterus has passed the level of the navel. Now those around you can easily understand that you are pregnant without telling you. You should have gained about 3.5 -5 kg by now. Urinary tract inflammation develops easily because the urinary flow rate slows down in the urinary tract that relaxes due to increased pregnancy hormones (especially progesterone).
Again, during this period, irregular contractions may be felt in the abdomen. If these contractions, which usually go away with rest, recur at regular intervals or are seen more than 4 times within an hour after resting, it is absolutely necessary to consult a doctor.
From this week onwards, the baby’s heart muscle begins to strengthen and pump blood more strongly. For this reason, the heart rate of the baby in the womb varies between 120-160. Height is 28 cm, weight is 400 gr.
WEEK 22
Cramps become more frequent. It can be extremely annoying at times. You can take foods rich in calcium and potassium to prevent cramps. A warm glass of milk, banana, grapefruit or orange before bed may be helpful. Stretching your legs in the opposite direction of the stiff muscle when the cramp occurs will help the cramp heal more quickly. Now you may find that you have trouble keeping your balance from time to time. Depending on the growth of your abdomen, the balance center of your body is shifting. Since the body cannot adapt to this at the same speed, you may have difficulty in maintaining your balance.
In this period, the baby is like a small model of a real person. Responds to sounds with movement and distinguishes beautiful sounds. You can talk to your child or even sing songs to him. You can calm the baby more easily with the same sounds after birth. The eyelids are formed and can move. If the baby is a boy, the testicles begin to descend into the scrotum from the intra-abdominal region, which is their first developmental place. This process is completed towards the end of 32 weeks. At the end of this week, the height is 29 cm and the weight is 470 gr.
WEEK 23
You should have gained approximately 4.5-5.5 kilograms since the beginning of pregnancy. Back pain may have worsened. These pains are due to the increase in the load of the spine and surrounding muscles in order to meet the weight carried in the anterior part of the abdomen in an unbalanced way. To relieve back pain, balanced movement, proper sitting patterns, massage and heat applications can be beneficial.
When your partner puts his hand on your belly, he can feel your baby’s movements very comfortably, and these movements can even be noticed from the outside. The reason for this is that the amniotic fluid in the baby is relatively high. So there is a lot of room for the baby to move around. Your baby can somersault in your tummy, move freely.
This week, the baby’s body is gradually returning to normal. However, the head is still slightly larger than the body, the middle ear bones also complete their development and the sounds begin to be transmitted to the baby’s auditory center. So your baby’s ears begin to hear. The skin is still wrinkled, it will continue to gain weight rapidly. Lanugo hairs take on a darker color. Height is 31 cm, weight is 550 gr.
WEEK 24
Your weight gain rate should be around 1-1.5 kilos per month. Consult your doctor if you gain weight rapidly and swelling begins to form on your body. Blood pressure monitoring and albumin in the urine may need to be investigated in terms of pregnancy poisoning (preeclampsia). Odorless, yellow-white colored, normal vaginal discharge can be seen in the vagina.
From this week onwards, it has been shown by scientific data that a significant part of the baby’s perceptions develop and the baby responds consciously, not reflexively, to stimuli. In other words, the baby has started to learn, to store information in his memory and to give correct reactions. His skin, which is quite wrinkled, is covered with a substance called vernix. The baby may suck his thumb, cough, hiccup. The baby can open his eyes. If he is born, his chances of survival are very low. Height: 32 cm, Weight: 600 gr.
WEEK 25
Due to the rapid growth of the uterus in the abdomen, heartburn and indigestion have increased even more. It is the period when children’s movements are best heard. Make sure to eat little and often, and keep your feet up while resting. There may be pain in the legs and waist due to the pressure of the growing uterus and the deterioration of circulation. In some pregnant women, there may be pain in the wrists and fingers. In such cases, it is very useful to keep the hand high and to apply cold application.
24-28. You need to have a 50 g glucose (sugar) loading test per week. With this test, even in pregnant women who did not have diabetes before, diabetes (gestational diabetes) that occurs only during pregnancy and can negatively affect the mother and the baby is investigated. Blood glucose is measured 1 hour after drinking 50 g glucose-containing beverage on an empty or full stomach (preferably after measuring fasting blood glucose following fasting). This measurement should be below 140 mg/dl.
The baby’s skin is now losing its transparent appearance. The skin is covered with folds. Heartbeats can be heard with a stethoscope or, if the baby’s position is suitable, by someone putting their ear to the tummy. Height: 33 cm. Weight: 700 gr.
WEEK 26
You may have pains in your ribs and abdomen as the baby is growing rapidly and its movements are stronger.
This week, the baby’s lung development accelerates. The lungs begin to produce a substance called surfactant, which is essential for their functioning. Also, from this week onwards, hand and foot prints begin to form. Brain functions are similar to those of a normal newborn. Features of the brain’s sleep and wakefulness periods can be distinguished. Height is about 34 cm, weight is 820 gr.
WEEK 27
During these weeks, you may suddenly feel a hardening in the abdomen. These are normal contractions of the uterus, but if you feel regular contractions that last longer than 30 seconds and are more frequent than 15 minutes, you should call your doctor right away as it could be preterm labor. During this period, breathing and sleep problems may be experienced. It is recommended to take a short walk before going to bed, or to increase the number of pillows used while lying down. It is also useful to measure blood pressure twice a week to control blood pressure.
This week, the brain and lungs continue to develop rapidly. The baby sucks his thumb and thus the jaw muscles develop.
Height: 35 cm. Weight: 1000 gr.
WEEK 28
Problems such as digestive problems, insomnia and difficult breathing continue to increase due to the baby growing in the abdomen. Constipation can be reduced by taking plenty of fluids, fresh vegetables and fruits. This week, your baby will continue to grow rapidly and fill the uterus as much as possible. Your uterus size has almost reached the level of your ribs. You may notice an increase in varicose veins and swelling in your legs this week. If you have a hemorrhoid problem, it may worsen and you may experience frequent cramps in your legs. If you have a blood incompatibility with your spouse this week, you should remind your doctor about this.
During this period, your baby’s need for calcium increases. If enough calcium is not taken, the calcium stores in the mother’s bones decrease.
The baby’s lungs are rapidly becoming ready for life outside in terms of structure and function. Deep sleep (dream) waves can be detected in the brain (REM). The probability of survival increased in case of premature birth. He may cry weakly, hiccup, his body begins to store fat. The baby begins to recognize sounds. Personality is thought to be formed from this week. Height: 36 cm. Weight:1100 gr.
WEEK 29
This period, called the last trimester, is up to 40 weeks. Most women gain an average of 5 kg during this trimester. The uterus continues to grow and press on the surrounding organs. Thus, the urge to urinate frequently, as in the first weeks of pregnancy, may reappear. You should notify your doctor of any vaginal bleeding and copious discharge or fluid that wets your underwear. The water bladder normally opens at or near birth. If it is opened early, there may be a serious risk of infection for the mother and baby.
Your baby can open his eyes and constantly turn his head in the womb. Fat layers continue to form. His senses are fully developed, he can perceive light, sound, taste and smell. Height: 38 cm. Weight: 1300 gr.
WEEK 30
Digestive problems in expectant mothers can be reduced by consuming high-fiber foods and drinking plenty of fluids. Complaints of cramps in the legs are quite common. Maintaining the intake of vitamins and minerals until birth is very important for the health of both mother and baby. Meanwhile, the mother’s weight has increased by 7-8 kilograms. It is possible to obtain rough information about the health of the child by counting the baby movements. If the baby moves 10 times in a day during the 12-hour period in which the mother is awake, this is interpreted as positive. If the baby is not moving or is moving less, you should consult your doctor.
You may notice that the baby is starting to come down more and more. In this case, there will be a feeling of lightness and increased pressure in the lower abdomen, and you may even have the feeling that the baby is going to be thrown out. Although breathing and eating become easier, walking may be uncomfortable and you may feel the need to urinate constantly.
Your baby weighs about 1350 g and is 45 cm long. Lanugo feathers disappear.
WEEK 31
Since the uterus is now large enough to fill the entire abdomen, the load on the respiratory, digestive and circulatory systems is gradually increasing. The mother may normally have gained around 8-10 kg. Your baby’s place has narrowed and he is pushing your organs up to make room for himself, compressing your stomach. You may have heartburn and indigestion.
Your baby can see inside the womb, separate the light from the dark. He may also blink and close his eyes. The baby moves less because there is not enough room for him to move. Its length is 45 cm and its weight is 1750 g. It is getting fatter due to the increasing subcutaneous adipose tissue. His sense of hearing is well developed, he can distinguish familiar sounds and music.
WEEK 32
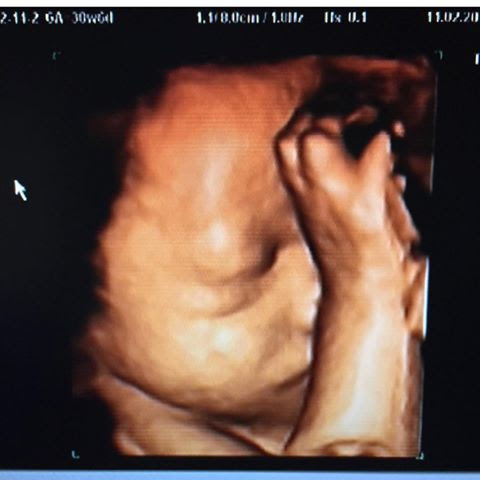 Starting this week, you should go to the doctor’s check-ups more often (with an interval of 2 weeks). In the last month, you should go to the doctor’s check-ups every week. During these months, the first milk called “colostrum” may come from the nipple in some mothers. The abdomen can be seen in different ways, depending on the baby’s size, position, and the amount of fluid in which he is swimming. Even if you have given birth before, you may perceive each pregnancy differently.
Starting this week, you should go to the doctor’s check-ups more often (with an interval of 2 weeks). In the last month, you should go to the doctor’s check-ups every week. During these months, the first milk called “colostrum” may come from the nipple in some mothers. The abdomen can be seen in different ways, depending on the baby’s size, position, and the amount of fluid in which he is swimming. Even if you have given birth before, you may perceive each pregnancy differently.
Back, groin, leg pains increase. The areas where your baby can move in the womb are rapidly decreasing. He opens and closes his eyes and makes breathing movements. The increase in fat and muscle tissue, whose hair has extended to the forehead border, accelerated. As the subcutaneous adipose tissue continues to develop, the color of your baby starts to turn from red to pink. Keep your legs elevated while resting. When lying down, you can support your left side with pillows, under or between your legs, on the side where your stomach rests on the bed.
Babies with the possibility of preterm birth during this period should definitely be delivered in hospitals where there is an intensive care unit. Brain development is accelerated, the iris of the eye responds to light and darkness. The baby sleeps and moves. Height: 46 cm, Weight: 1800 gr.
WEEK 33
As the relaxin hormone, which increases during pregnancy, relaxes your thigh joints, your walking becomes difficult. You start walking with your hands on your waist and pushing your waist forward. You should rest in a comfortable position, especially at night. If you have swelling in your hands and feet, your blood pressure should be monitored more closely. Your baby’s chances of living outside are increasing. A substance called surfactant secreted from the lungs (alveoli) has begun to increase. With the increase of these substances, the baby’s ability to live in the external environment without respiratory distress will increase.
The baby is now about 2000 g. weighs in and measures 47cm in length. He exercises his lungs by practicing breathing. From this week, roughly half of your weekly weight gain of 500 g goes to the baby. For the next seven weeks, your baby will gain more than half of his birth weight, preparing himself for life outside the womb. Due to these fat deposits, the skin thickens and turns pink. In male fetuses, the testicles have entered the ovarian sac. The skin color changes from red to pink.
WEEK 34
The most common complaint in this period is fatigue, insomnia and pain complaints increase. Rest and short walks in the open air every day provide relaxation in your muscles. Weight gain continues. Pain called “Braxton Hicks” causes the uterus to harden from time to time.
As the birth approaches, your doctor who carries out your pregnancy follow-up should start to inform you about the birth.
Maintaining the intake of vitamins and minerals until birth is important for the health of both mother and baby. Weakness and fatigue are felt more frequently, especially after the 34th week. Doctor check-ups should be more frequent for your and your baby’s health. During these examinations, your blood pressure is measured, the growth of the uterus is checked, and your baby’s weight gain, the amount of amniotic fluid, the position of your baby in the uterus, the placement and quality of the placenta are evaluated by ultrasound measurements. If necessary, your baby’s heartbeat and uterine contractions are evaluated with NST (non-stress test).
Your baby weighs about 2300 g and averages 47 cm. is long. It’s probably in the head down position. However, it can continue to change positions. The skull bones are still quite soft and not fully fused, making it easier for the baby to exit the narrow birth canal. You may notice that your feet, hands, face, and ankles are swollen, and this edema gets worse in hot weather and later in the day. You should drink plenty of fluids for your baby and kidneys. Significant edema in the body, excessive weight gain, and high blood pressure may be signs of preeclampsia. When you encounter these findings, you should be followed carefully by your doctor.
WEEK 35
Your weekly weight gain is 350-500 g, and the baby gains half the weight you gain each week (180-250 g). It is okay to have sexual intercourse unless your doctor tells you otherwise. To relax, it will be good to take a shower, rest, and take short walks in the open air. You should monitor the baby’s movements, and if you notice a significant decrease in baby movements or not playing at all, you should definitely inform your doctor.
Your baby weighs over 2500g and is probably close to 50cm in length. 99 percent of babies born this week survive. The lungs are usually fully developed and breathing problems, which are the cause of death in babies born before 35 weeks or premature, are more easily resolved after this week.
Your baby continues to store fat. All organ systems have completed their development and maturation. Since it starts to take up more space in the uterus compared to the water in which it swims, its movements will not be easy. Your baby is about 2600 grams. Weight gain, especially fat storage, will begin at the level of the shoulders.
WEEK 36
After this week, your doctor may call you for a check-up to evaluate you with ultrasound every week. Your uterus has expanded to 1000 times its original volume and you may feel like you have no room left, the uterus is probably under your ribs. Probably 12 to 16 kg total. you have gained weight.
Your baby is about 2800 grams. Fat now begins to be stored on the cheeks, the body is fuller due to the storage of adipose tissue under the skin, and wrinkles on the facial skin disappear. The baby gradually enters the birth canal.
WEEK 37
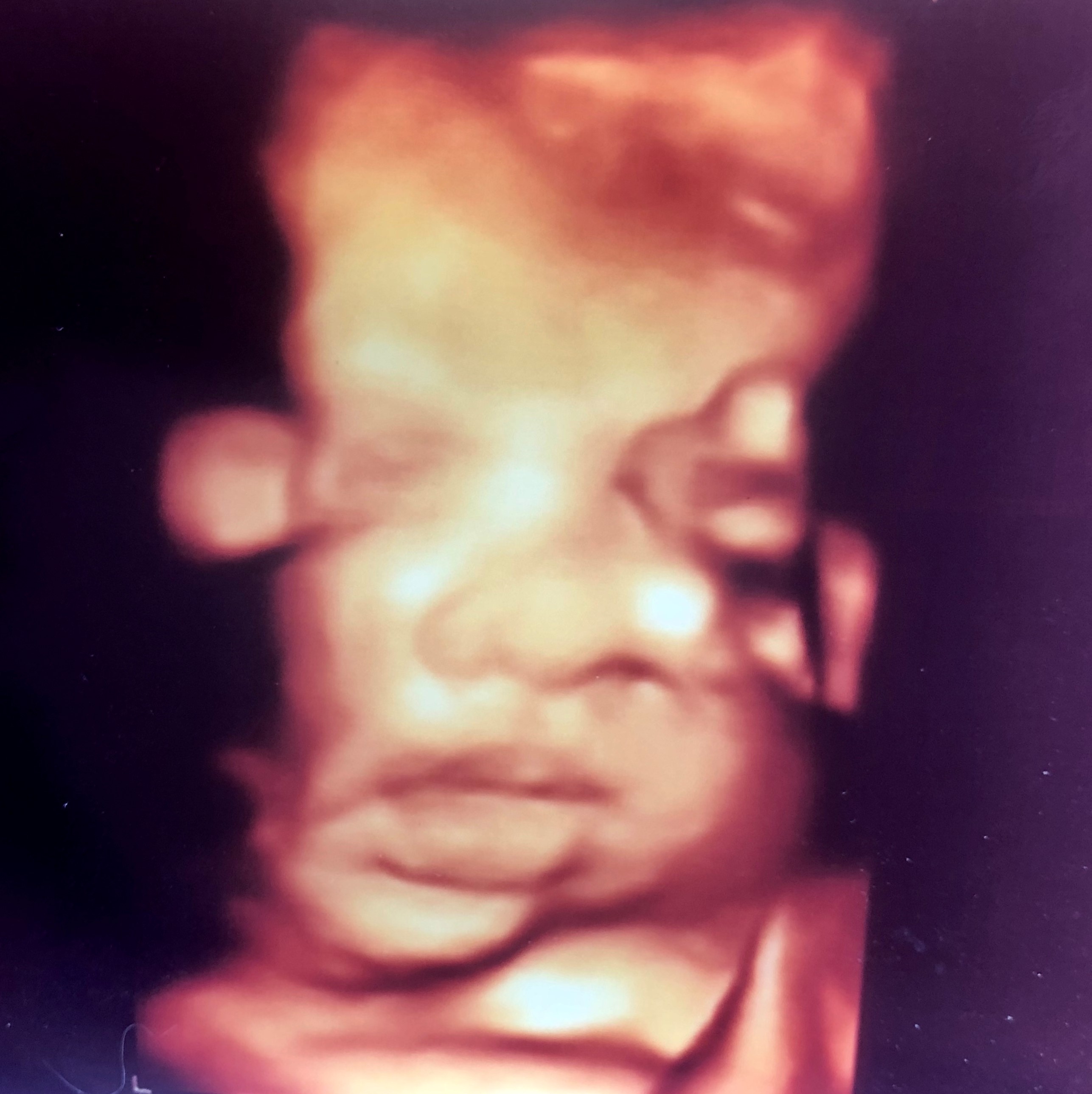 From now on, it is okay for your baby to be born any day from this week on. Approximately 3000 gr. weighs 51 cm. is long. During your weekly doctor visits, your doctor may want to check the condition of your baby, whether there is an opening in the cervix, and how far the baby is from the birth canal. During this period, you should talk to your doctor clearly about the mode of delivery. While your doctor performs routine checks of your baby with an ultrasound examination, NST should be performed at appropriate intervals if necessary. Monitoring your baby’s breathing movements with ultrasound is also an indication that your baby is in good health.
From now on, it is okay for your baby to be born any day from this week on. Approximately 3000 gr. weighs 51 cm. is long. During your weekly doctor visits, your doctor may want to check the condition of your baby, whether there is an opening in the cervix, and how far the baby is from the birth canal. During this period, you should talk to your doctor clearly about the mode of delivery. While your doctor performs routine checks of your baby with an ultrasound examination, NST should be performed at appropriate intervals if necessary. Monitoring your baby’s breathing movements with ultrasound is also an indication that your baby is in good health.
Since your baby has grown in size, it will be difficult for him to move in the womb and you may notice a decrease in baby movements. Your baby starts to feel more and more as they move. It may wake you up more often at night. His body is well shaped, and his efforts to settle in the birth canal continue. Fingernails and toenails have now grown to the tips of the fingers.
WEEK 38
You can now give birth at any time, and this is now defined as a timely birth. Studies show that only 5% of births occur on the expected due date. 60% of births occur 1 week before the expected due date.
This week, your baby’s head circumference and abdominal circumference are approximately equal. Your baby weighs over 3000 g and is about 51 cm long. Most of the hairy lanugo layer covering the baby has disappeared, and the cheese-like layer (vernix caseosa) has also disappeared (some may remain at birth). Both will be swallowed by the baby along with other secretions and retained in the baby’s intestines. These form a black stool that is expelled with the baby’s first bowel movements. We call this “meconium”.
WEEK 39
Your baby is probably positioned so that his head is in the birth canal. The immune system is still not fully developed and continues to receive antibodies (immune cells) from the mother through the placenta. Antibodies passed through you will help your baby fight infections for at least 6 months after birth. After birth, the baby will continue to receive some antibodies (Ig A) from breast milk.
In the last week, the amniotic membrane (water sac) may open at any time and your water may come out. Sometimes the water coming out of the glass is fast and in large quantities, sometimes it can be very slow. You may even feel like you are leaking urine. Regardless of the amount, if you think that your water is coming, you should call your doctor or go to the hospital without wasting time.
Now the baby has started to sleep very often. The big day is very near. Its height is about 51 centimeters and its weight is 3,250 grams.
WEEK 40
 Your baby is ready for his birthday. Its skin is pink-red, its length is about 52 centimeters, and its weight is 3,300-3,500 grams.
Your baby is ready for his birthday. Its skin is pink-red, its length is about 52 centimeters, and its weight is 3,300-3,500 grams.
When a decision is made for normal delivery, the baby’s movements, heartbeats and the amount of amniotic fluid are evaluated with ultrasound and NST (non-stress test). If labor pains have not started at the end of this period, artificial pain is tried first. If labor does not start despite artificial pain, or if the baby does not progress in the birth canal, or if the baby’s heartbeat begins to deteriorate, the baby is delivered by cesarean section.
As the moment of birth approaches, the cervix begins to open gradually. When this opening reaches approximately 10 cm, the first stage of labor is complete. With the second stage that starts after that, the baby progresses in the mother’s birth canal and is born after completing the 40-week period in the mother’s womb.
Below is the contact information for Pregnancy Follow -up with Jin.Op.Dr. Yeşim Yercok. Address: Fener Kalamış cad. Billur apt. No:5 Da:9 Kızıltoprak/ İSTANBUL Telephone: +90 216 385 17 15
E-Mail:
info@dryesimyercok.com
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]